This module implements the rdk:component:camera API in a viam:camera:realsense model.
Configure this model on your machine to stream image and depth data from the Intel RealSense family of cameras to Viam.
Navigate to the CONFIGURE tab of your machine in the Viam app.
Add camera / realsense to your machine.
On the new component panel, copy and paste the following attribute template into your camera’s attributes field:
{
"sensors": ["color","depth"],
"width_px": 640,
"height_px": 480,
"little_endian_depth": false
}Edit the attributes as applicable.
Note
For more information, see Configure a Machine.
The following attributes are available for viam:camera:realsense cameras:
| Name | Type | Inclusion | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
sensors |
list | Required | The RealSense data streams you want your robot to sense from. A list that contain the strings color and/or depth. The sensor that comes first in the list is designated the "main sensor", and is the image that gets returned by get_image calls and appears in the CONTROL tab on the Viam app. If you would like a list of images from all listed sensors simultaneously, use GetImages. |
width_px |
int | Optional | The width of the output images in pixels. If the RealSense cannot produce the requested resolution, the component will fail to be built. |
height_px |
int | Optional | The height of the output images in pixels. If the RealSense cannot produce the requested resolution, the component will fail to be built. |
little_endian_depth |
bool | Optional | A bool that specifies whether raw depth data should be encoded in a little-endian byte order. By default it is false, and encodes the raw depth data in a big-endian byte order. |
{
"components": [
{
"name": "myRealSense",
"attributes": {
"sensors": ["color","depth"],
"width_px": 640,
"height_px": 480,
"little_endian_depth": false
},
"namespace": "rdk",
"type": "camera",
"model": "viam:camera:realsense"
}
]
}
Before testing the module, make sure that your machine is connected to the Viam app, displaying as Live in the part status dropdown in the top right corner of the machine's page.
Once the realsense model is configured on your machine, you can access the depth and color data the camera streams through the Viam camera API.
The following methods of the Viam camera API are supported:
GetPointCloud: returns depth data and can return color data depending on the provided imageGetImage: returns color dataGetImages: returns both depth and color dataGetProperties: returns intrinsic properties of a camera
You can view the data your camera streams live on the CONTROL tab of the Viam app. For more information, see Control Machines.
If you are using a Linux machine, and do not want to use the Viam registry, you can download the module AppImage from our servers directly to your machine:
sudo curl -o /usr/local/bin/viam-camera-realsense http://packages.viam.com/apps/camera-servers/viam-camera-realsense-latest-aarch64.AppImage
sudo chmod a+rx /usr/local/bin/viam-camera-realsense
If you need the AppImage associated with a specific tag, replace latest in the URL with the tag version, i.e. 0.0.X.
Then, follow the instructions to add a local module to add the local instance of the realsense module to your machine.
Provide an Executable path of /usr/local/bin/viam-camera-realsense when adding the module.
Or, if you aren't using the Viam app to manage your machine's configuration, modify your machine's JSON file as follows to add the realsense module to your machine:
"modules": [
{
"type": "local",
"name": "intel",
"executable_path": "/usr/local/bin/viam-camera-realsense"
}
],
The repo comes with a suite of integration tests that allow one to test if the module works with an actual realsense device on the machine of interest. These integration tests are compiled into a binary and can be downloaded here:
curl -o realsense-integration-tests http://packages.viam.com/apps/camera-servers/realsense-integration-tests-latest-aarch64.AppImage
sudo chmod a+x realsense-integration-tests
./realsense-integration-tests -module /path/to/the/module
The binary takes one argument, which is the location to the module you would like to test out. Make sure only one RealSense device is connected to the machine you will be running the tests on.
If you would like to compile the integration tests yourself, you will need to compile the binary on the same machine you expect to run it on.
- Copy the repo to your local robot:
git clone https://github.com/viam-modules/viam-camera-realsense.git - run
make realsense-integration-tests - run the tests with
./realsense-integration-tests -module /path/to/realsense/module
Support for specific hardware is known for the following devices. The table is not complete and subject to change. In order to test out the module for your specific set up, it is recommended you run the integration tests provided.
| Devices | D435 | D435i | D455 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RPi 4B Bullseye | X | ||
| Orin Nano JetPack 5.1 | X | X | X |
| UP 4000 | X |
This module depends on the librealsense SDK. As of the time of writing, Ubuntu is the only Linux Distro librealsense officially supports. The module works on our hardware setups using Bullseye on RPI4, and some setups on Bookworm. However, we recommend adhering to the requirements of the SDK dependency and to use Ubuntu when possible to avoid instability and unexpected behavior.
If you get an error like "failed to set power state", or "Permission denied", you may need to install the udev rules for when the USB plugs in.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/7a7c2bcfbc03d45154ad63fa76b221b2bb9d228f/config/99-realsense-libusb.rules
sudo cp 99-realsense-libusb.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/
sudo udevadm control --reload-rules
sudo udevadm trigger
You can also look at the official RealSense troubleshooting guide here.
The module takes advantage of faster USB ports. Use the (blue) USB 3.0 port on the Raspberry Pi for faster streaming and access to more resolution options.
You can also build it yourself using Docker and Viam canon. Use the commands
docker pull ghcr.io/viam-modules/viam-camera-realsense:arm64
git clone https://github.com/viam-modules/viam-camera-realsense/
cd viam-camera-realsense/
canon -arch arm64 make appimage-arm64
This will use the Docker container to compile a binary for the aarch64 architecture. If you want to compile for x86_64/amd64 architecture, change arm64 to amd64 in the above commands. The AppImage will be put in the packaging/appimages/deploy directory.
If you would like to try to gather all of the dependencies yourself and not use Docker, you will need:
- librealsense
git checkoutand install from source.- be sure to use cmake flags
cmake .. -DBUILD_EXAMPLES=false -DBUILD_GRAPHICAL_EXAMPLES=false -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
- libjpegturbo
- libprotobuf
- Viam C++ SDK
- specifically
libviamsdk,libviamapi, andlibviam_rust_utils
- specifically
then do make viam-camera-realsense to compile the binary, and make appimage to create the AppImage.
When developing, you also have the option to build the module with ASAN/LSAN enabled to test for memory leaks. You can do so by running a build command such as canon -arch arm64 make clean appimage-arm64 SANITIZE=ON with the SANITIZE flag =ON. ASAN/LSAN logs will then be included as error logs in your robot logs on the Viam App. Additionally, running the integration test binary against the debug ASAN/LSAN build will fail if a leak is detected. Currently the debug ASAN/LSAN build is only supported on linux/arm64.
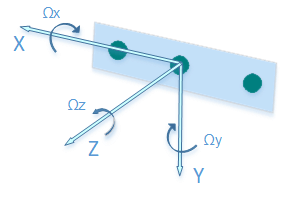
It is important to consider that the coordinate system of the camera might not match the coordinate system of the component it is mounted on. Let us consider the scenario where the camera is mounted on a base, such that the camera faces the forward direction of movement of the base. Let the base's forward direction be the +Y axis. Following the right hand rule, the +X axis points right, and so the +Z axis of the base points up. For the intel realsense camera the +Z axis points out the camera lens, the +X axis points to the right, and the +Y axis points down. To properly configure these components in the frame system we say that the camera's parent is the base. We say that the orientation of the camera in Viam's Orientation Vector Degrees is OX:0, OY:1, OZ:0, Theta:-90. It is important to note that the base itself must also be in the frame system, the base would have parent as world with the default Viam Orientation Vector Degrees values, i.e. OX:0, OY:0, OZ:1, Theta:0.
Below is an image of the intel realsense's coordinate system.