GitHub Action
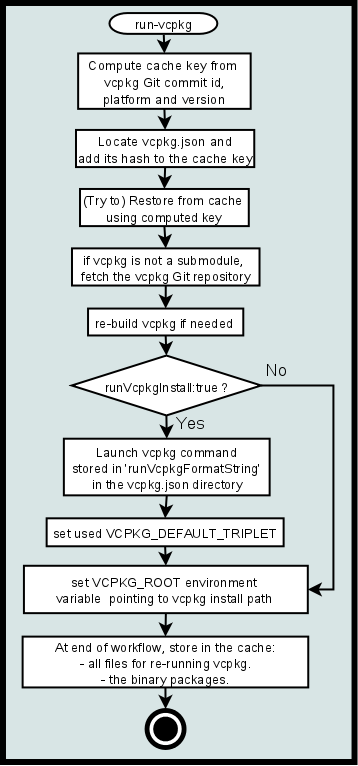
run-vcpkg
The run-vcpkg action restores from cache vcpkg along with the previously installed ports. On the other hand when there is a "cache miss":
vpckgis fetched and installed; the cache's key is composed by hashing the hosting OS name, the command line arguments and the vcpkg's commit id.- Restoring from cache can be skipped with
doNotCache: true.
- Restoring from cache can be skipped with
- Then
vcpkgis run to install the desired ports.- This step can be skipped with
setupOnly: true.
- This step can be skipped with
- Artifacts and
vcpkgare then saved in cache.- Saving to cache can be skipped with
doNotCache: true. - Saving to cache happens at the end of the workflow in case
setupOnly: true, otherwise it happens at the end of the action execution.
- Saving to cache can be skipped with
The provided samples use GitHub hosted runners.
Good companions are the run-cmake action and the get-cmake actions.
- Contributing
- Quickstart
- Best practices
- Action reference: all input/output parameters
- Samples
- Projects
Read CONTRIBUTING.md
It is highly recommended to use both vcpkg as a submodule and a vcpkg.json manifest file to declaratively specify the dependencies.
Both suggestions are shown in the hosted-advanced-setup-vcpkg-manifest.yml workflow, here below an excerpt:
jobs:
build:
env:
buildDir: '${{ github.workspace }}/build/'
steps:
#-uses: actions/cache@v1 <===== YOU DO NOT NEED THIS!
# Install latest CMake.
- uses: lukka/get-cmake@latest
# Restore from cache the previously built ports. If a "cache miss" occurs, then vcpkg is bootstrapped. Since a the vcpkg.json is being used later on to install the packages when run-cmake runs, no packages are installed at this time and the input 'setupOnly:true' is mandatory.
- name: Restore artifacts, or setup vcpkg (do not install any package)
uses: lukka/run-vcpkg@v6
with:
# Just install vcpkg for now, do not install any ports in this step yet.
setupOnly: true
# Location of the vcpkg submodule in the Git repository.
vcpkgDirectory: '${{ github.workspace }}/vcpkg'
# Since the cache must be invalidated when content of the vcpkg.json file changes, let's
# compute its hash and append this to the computed cache's key.
appendedCacheKey: ${{ hashFiles( '**/vcpkg_manifest/vcpkg.json' ) }}
vcpkgTriplet: ${{ matrix.triplet }}
# Ensure the vcpkg artifacts are cached, they are generated in the 'CMAKE_BINARY_DIR/vcpkg_installed' directory.
additionalCachedPaths: ${{ env.buildDir }}/vcpkg_installed
- name: Run CMake to install the dependencies specified in the vcpkg.json manifest, generate project file and build the project
uses: lukka/run-cmake@v3
with:
cmakeListsOrSettingsJson: CMakeListsTxtAdvanced
cmakeListsTxtPath: '${{ github.workspace }}/vcpkg_manifest/CMakeLists.txt'
buildDirectory: ${{ env.buildDir }}
# This input tells run-cmake to consume the vcpkg.cmake toolchain file set by run-vcpkg.
useVcpkgToolchainFile: true
buildWithCMake: trueWhen setupOnly: true, it only setups vcpkg without installing any port. The provisioned vcpkg can then be used in a subsequent step as shown:
# Restore from cache the previously built ports. If cache-miss, download and build vcpkg (aka "bootstrap vcpkg").
- name: Restore from cache and install vcpkg
# Download and build vcpkg, without installing any port. If content is cached already, it is a no-op.
uses: lukka/run-vcpkg@v6
with:
setupOnly: true
# Now that vcpkg is installed, it is being used to run with the desired arguments.
- run: |
$VCPKG_ROOT/vcpkg install boost:linux-x64
shell: bashWhen using vcpkg, be aware of how it works, specifically:
- a specific version of
vcpkgmust be used either locally and on build servers; - a specific version of
vcpkgis identified by the commit id of the used vcpkg repository; - it not possible to choose which version of a port to install, instead it is the used version of
vcpkgthat establishes which version (just one) of a port is available;
To sum up, you need to pin the specific version of vcpkg you want to use to keep a consistent development experience between local and remote build environments. This is accomplished by using vcpkg as submodule of your Git repository; this way the version of vcpkg used is implied by the commit id specified by the submodule for vcpkg.
The vcpkg.json is a manifest file that declaratively specifies the dependencies to be installed. The file is being used automatically by running CMake when:
- starting CMake with the
vcpkg.cmaketoolchain file. - the root CMake source directory contains a vcpkg.json file.
When conditions are satisfied, the toolchain execution starts vcpkg to install the packages declared in the manifest file.
Putting this manifest-like file under source control is highly recommended as this helps to run vcpkg the same exact way locally and remotely on the build servers.*
The dependencies specified in the vcpkg.json file are installed when CMake runs (i.e. at run-cmake time), hence the 'run-vcpkg' step must have the input setupOnly: true.
View the workflows based on the run-cmake and run-vcpkg actions.
| CMakeSettings.json samples | |
|---|---|
| Linux/macOS/Windows, hosted runner, with vcpkg as submodule |
All the content in this repository is licensed under the MIT License.
Copyright (c) 2019-2020-2021 Luca Cappa
Other than submitting a pull request, donating is another way to contribute to this project.