We propose an energy-efficient self-organized framework for sub-channel allocation and power allocation for ultra-dense small cell network, which can operate in both licensed and unlicensed bands. In order to protect the legacy WiFi devices (operating in unlicensed bands), we consider LTE in unlicensed band based on carrier sense adaptive transmission, a technique in which 'ON' and 'OFF' duty cycle approach is utilized for harmonious coexistance of LTE and WiFi. On the other hand, there are severe interference management problems among small cells (operating in licensed bands) and between small cells (operating in licensed bands) and macrocells due to co-channel and ultra-dense deployment of small cells. In the light of these concernes, designing a self-organizing framework for sub-channel allocation and power allocation is a challenging task. We propose a self-organized optimization framework for sub-channels and power levels by utilizing a non-cooperative game with the concern of minimizing the energy efficiency of small cells without creating harmful impact on macro cell users, small cell users, and legacy wifi users, respectively.
Considering the co-channel environment, the two main interference components that are present in the ’ON’ period of LTE-U based CSAT are: crosstier and co-tier components. The former one is comprised of interference between small cells and macro cells (operating in licensed bands) and between small cells and legacy WiFi devices (operating in unlicensed bands). The later one is comprised of interference among small cells (operating in licensed and unlicensed bands). The ’ON’ period of LTE-U, which is based on a number ofWiFi characteristics including traffic load, node density, etc and is proposed here to be determined by a centralized MBS based upon the measurement (that represents the presence of WiFi access points) received from dual-access small cells. This proposition make sense because the centralized MBS can have a complete picture about the WiFi characteristics which are provided by the SBSs. In addition, it is also suitable to have such ’ON’ period determination at the centralized level because its update is not necessarily as frequent as for the sub-channels and power levels. Since the determination of ’ON’ and ’OFF’ duty cycle is based on the detection of WiFi signals by dualaccess small cells, it is possible that the traffic of some WiFi access points is not detected as they are not in their sensing range but they do have impact on the small cells operating in unlicensed band. In order to address this we are also considering the WiFi access points in our network model that are not in the sensing range of small cells and they have direct impact on them.
In the proposed self-organizing framework, each dualaccess small base station has to perform three tasks iteratively: sensing, learning, and tuning. In the sensing task, each dual-access small cell base station interacts with the environment and acquire channel gains from both licensed and unlicensed bands. Each SBS detects the WiFi traffic and this information is conveyed to a centralized MBS for
adjusting the ’On’ and ’OFF’ duty cycle. In the learning task, an iterative mechanism is taken into account for the allocation of sub-channels and power levels with the concern of enhancing the energy efficiency without affecting the QoS requirements of the small cell users and the macro cell users, respectively. In the tuning task, the best learned strategies from the task 2 are updated by each dual-access small cell. The objective of the proposed self-organizing framework is to enhance the energy efficiency by exploiting sub-channels and power levels of ultra-dense small cells without creating harmful impact on other network entities. In order to achieve this, a less-complex iterative algorithm using a non-cooperative game is proposed, which is suitable for the self-organizing environment.
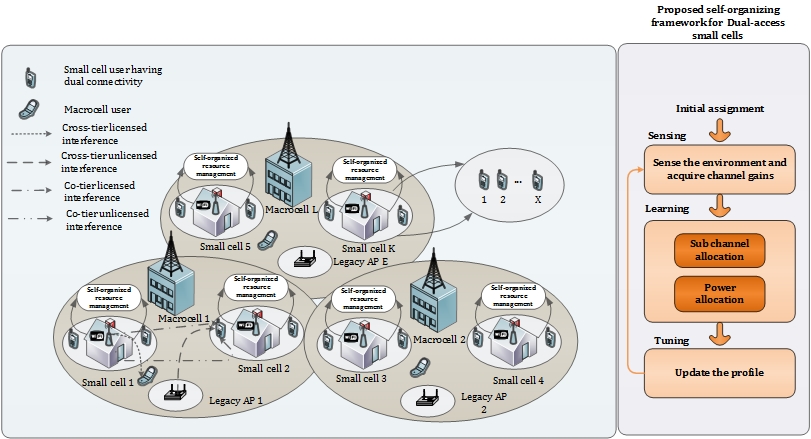
Since the framework is part of a paper recently submitted and once it is accepted and published, we will release the technical details.
Adnan Shahid, Vasilis Maglogiannis, Irfan Ahmed, Kwang Soon Kim, Eli De Poorter, Ingrid Moerman, "Energy-efficient resource allocation for ultra-dense licensed and unlicensed dual-access small cell networks", submitted to IEEE Transaction on Mobile computing, 2018.
If you need any further information, then you can contact at [email protected]