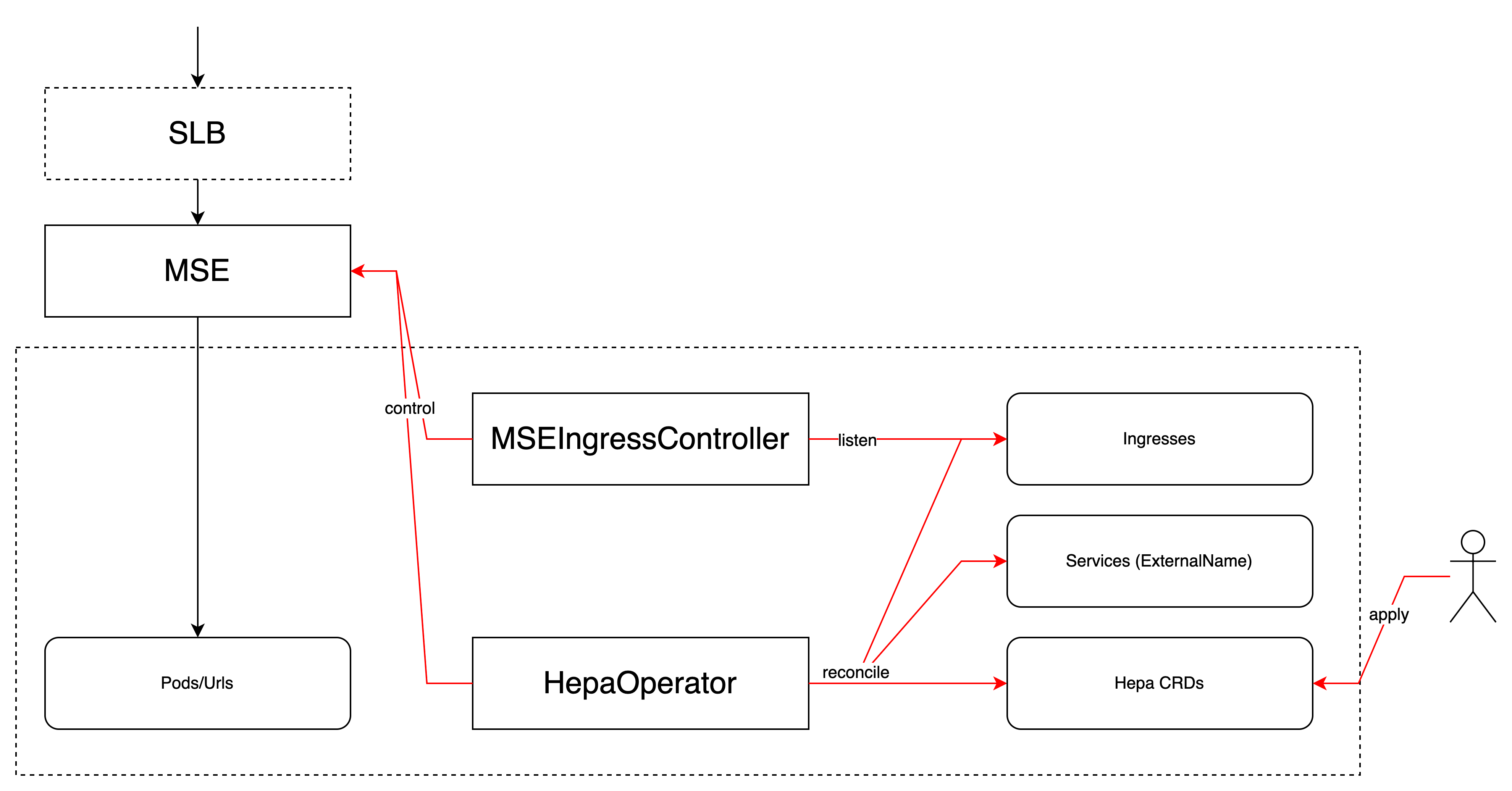
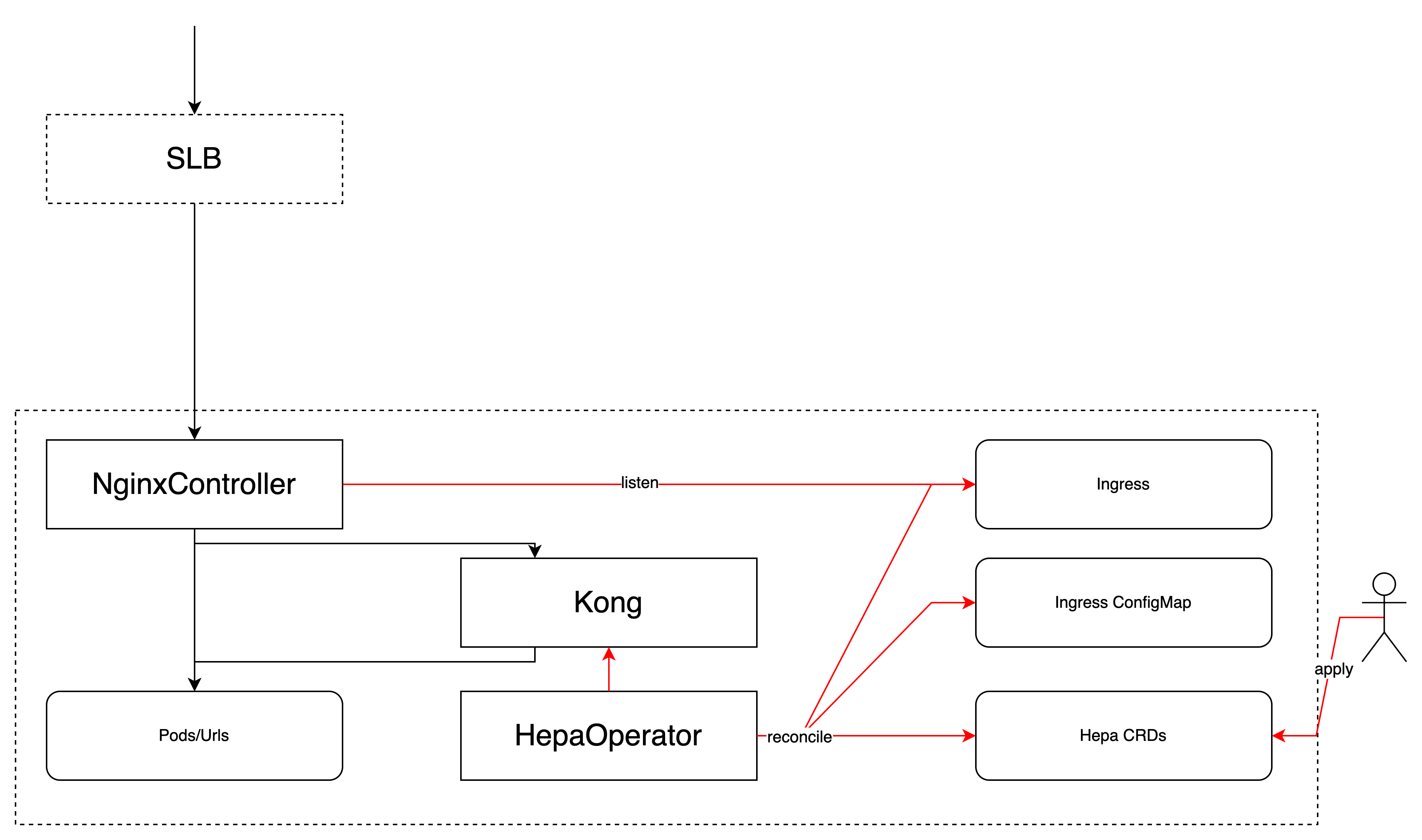
The Hepa Operator is a Kubernetes Operator, implemented using the kubebuilder scaffolding tool.
Hepa Operator is designed to abstract the reverse proxy of a cluster API gateway and the policies attached to the HTTP interface. Currently supported and intended gateway products are:
- Aliyun MSE
- Kong
Prerequisite: K8s must be installed first. You can install K8s using tools such as KIND or Docker Desktop.
make release-completeltyA release.yml file is generated in the project root, which contains all the K8s resources needed to install Hepa Operator (including CRDs, Namespace, Deployment, Role, etc.).
make applyAll K8s resources of Hepa Operator will be created or updated.
make manifest; make install; make runto run locally.
make apply-samplesor
make get-samplesoutput:
[root@node-172016174045 hepa-operator]% make get-samples
kubectl apply -f config/samples/_v1_hapi.yaml
namespace/hapi-operator-sample unchanged
deployment.apps/go-httpbin unchanged
service/go-httpbin unchanged
configzone.hepa.erda.cloud/hapi-operator-sample unchanged
hapi.hepa.erda.cloud/hapi-sample unchanged
kubectl -n hapi-operator-sample get czr,hapi,ing,svc,deploy,pod
NAME SCENE HOSTS HAPI_COUNT POLICIES PHASE
configzone.hepa.erda.cloud/hapi-operator-sample 1 ["AUTH","SAFETYIP"] OK
NAME ENDPOINT REDIRECTTO POLICIES PHASE
hapi.hepa.erda.cloud/hapi-sample hapi-sample.mse-daily.terminus.io/s baidu.com/s ["SAFETYIP","auth"] OK
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress.networking.k8s.io/hapi-sample mse hapi-sample.mse-daily.terminus.io **.**.**.**,**.**.**.** 80, 443 9d
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/external-hapi-sample ExternalName <none> baidu.com 80/TCP,443/TCP 10d
service/go-httpbin ClusterIP **.**.**.** <none> 80/TCP 37d
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/go-httpbin 1/1 1 1 37d
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/go-httpbin-68fdb87875-g7b8f 1/1 Running 0 11dkubectl delete --ignore-not-found -f release.ymlapiVersion: hepa.erda.cloud/v1
kind: ConfigZone
metadata:
name: hapi-operator-sample
namespace: hapi-operator-sample
spec: # spec describes some configuration information, which can be referenced by Hapi
policy:
auth:
authType: hmac-auth
switch: true
safetyIP:
blackListSourceRange: ""
domainBlackListSourceRange: ""
domainWhiteListSourceRange: ""
ipType: x-peer-ip
keyRateLimitingValue: 10 query_per_second
switch: true
whiteListSourceRange: 123.45.67.1/16,10.10.10.10apiVersion: hepa.erda.cloud/v1
kind: Hapi
metadata:
name: hapi-sample
namespace: hapi-operator-sample
labels:
"configZone": "hapi-operator-sample" # ## referenced ConfigZone
"packageId": "c82396e5fc13ef7bbf6bc078502a21e4" # ## custom labels
spec: # spec describes the rules of the reverse proxy
hosts: # # routed domains
- hapi-sample.mse-daily.terminus.io
path: /search # # routed path
backend: # # backend describes forwarding rules
redirectBy: url # ## redirectBy "url" for an external url or "service" for a k8s Service
serviceName: go-httpbin # ## reverse-proxy to go-httpbin:80 in this namespace if redirectBy "service"
servicePort: 80
upstreamHost: baidu.com # ## reverse-proxy to baidu.com if redirectBy "url"
rewriteTarget: /s # ## rewrite path from "/search" to "/s" while doing reverse-proxy
policy: # # policy describes the route policy
auth: # ## a policy named "auth"
authType: sign-auth
global: false # ## use the policy from the referenced ConfigZone if global=true
switch: true # ## enable the policy if switch=true
safetyIP:
blackListSourceRange: ""
domainBlackListSourceRange: ""
domainWhiteListSourceRange: ""
ipType: x-peer-ip
keyRateLimitingValue: 12 query_per_second
global: true
switch: false
whiteListSourceRange: 123.45.67.1/18A reverse proxy rule is represented by defining a CRD called Hapi, which describes a reverse proxy rule and the policies attached to the rule.
Hepa-Operator listens to this CRD and controls some K8s API objects (e.g. Ingress, Service) and some external resources (e.g. Aliyun MSE Gateway Openapi, Kong Admin API) to implement the reverse proxy.
% kubectl -n hapi-operator-sample get czr,hapi,ing,svc
NAME SCENE HOSTS HAPI_COUNT POLICIES PHASE
configzone.hepa.erda.cloud/hapi-operator-sample 1 ["AUTH","SAFETYIP"] OK
NAME ENDPOINT REDIRECTTO POLICIES PHASE
hapi.hepa.erda.cloud/hapi-sample hapi-sample.mse-daily.terminus.io/search baidu.com/s ["SAFETYIP","auth"] OK
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress.networking.k8s.io/hapi-sample mse hapi-sample.mse-daily.terminus.io **.**.**.**,**.**.**.** 80, 443 9d
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/external-hapi-sample ExternalName <none> baidu.com 80/TCP,443/TCP 10dwhere czr is the short name of the ConfigZone (Config Zone Reference).
The print column of ConfigZone HAPI_COUNT indicates the count of HAPIs that reference this configuration;
POLICIES indicates the list of policies enabled on this instance.
The print columns Hapi ENDPOINT and REDIRECTTO represent a pair of routing relationships,
as in the example, that forwards requests for "hapi-sample.mse-daily.terminus.io/search" to "baidu.com/s";
POLICIES indicates the list of policies enabled on the route, capitalization indicates a reference to the global policy, and lowerCamelCase indicates a local policy.
How does it implement this forwarding relationship ? When the gateway is adopted Aliyun MSE, for redirectBy "service", Hepa Operator will create an Ingress for reverse proxying to the Service; for forwarding by url (as in this sample), Hepa Operator will first create an additional ExternalName Service, whose ExternalIP is the target domain, and then creates an Ingress for reverse proxying to the Service. When the gateway is adopted Kong, it will create an Ingress for reverse-proxying to Kong, and then creates Kong Service, Route and some other objects for reverse-proxying to the real back-end service.