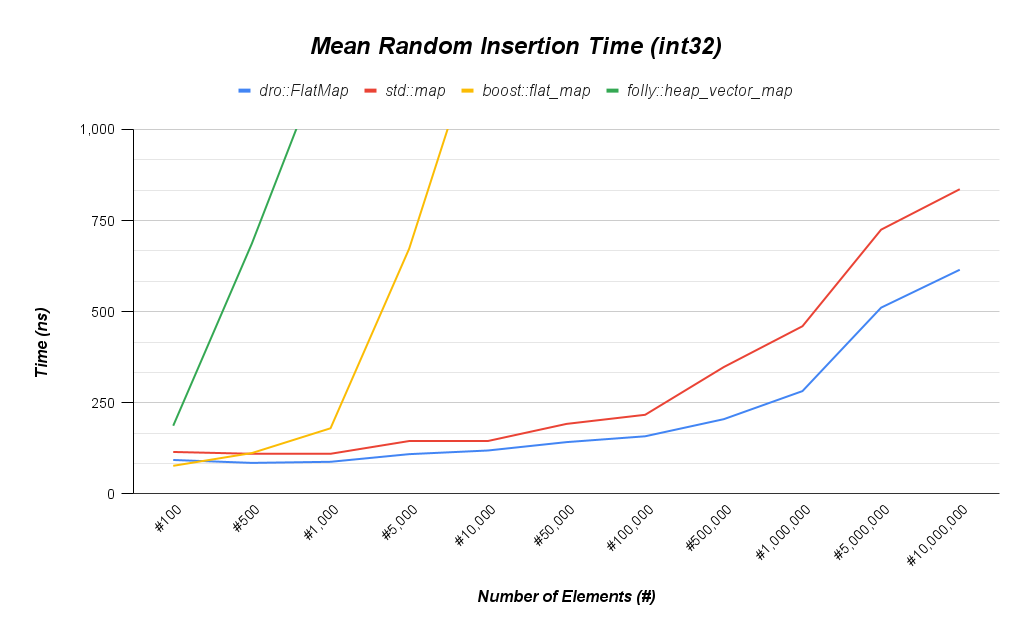
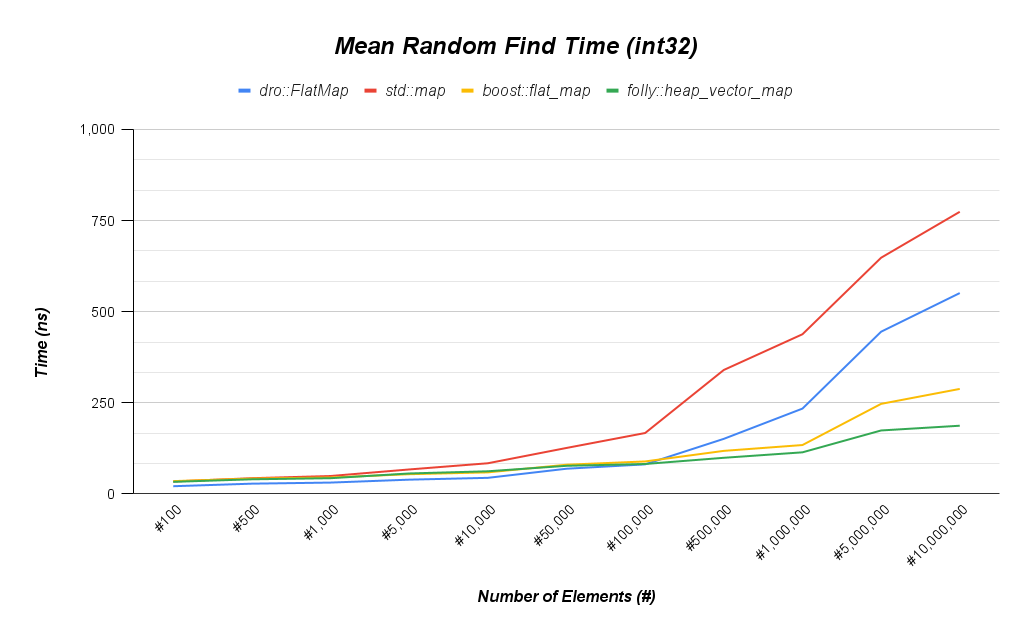
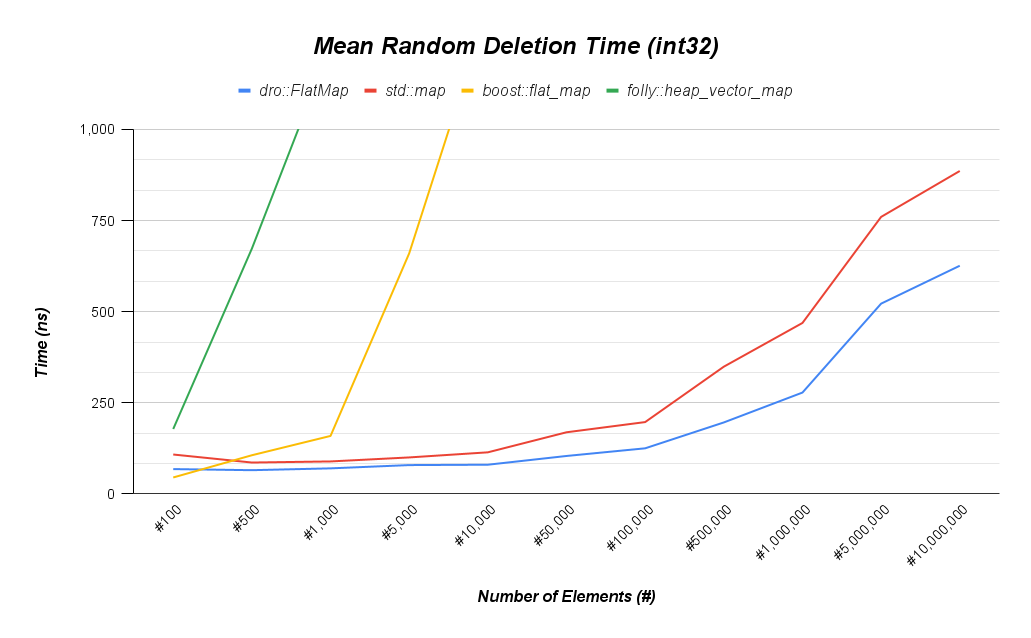
A STL compliant map and set that uses a red black tree under the hood. Much faster than boost::flat_map for any insert or delete heavy workload over ~250 elements. Beats std::map for all workloads when full optimizations are enabled.
This flat map uses a vector to store the tree nodes, and maintains an approximate heap structure for a cache optimized binary search.
In order to validate the correctness of the balancing algorithm, a full tree traversal is performed comparing the dro::FlatMap to the STL Tree implementation. Many red black trees have subtle errors due to lack of validation.
ToDo:
- 100% code coverage - currently ~50%.
- Full support for "copy only" and "move only" keys and values
Main points:
- The key and value must be default constructible.
- The key and value must be copy or move assignable.
- Memory isn't deallocated on erase. Must call shrink_to_fit to free memory, or wait on destructor.
- Weakness: All the iterators are invalidated on all modifying operations.
The full list of template arguments are as follows:
- Key: Must be default constructible and a copyable or moveable type
- Value: Must be default constructible and a copyable or moveable type
- MaxSize: Integral type used for tree size optimizations.
- Compare: Function used to compare keys, default std::less
- Allocator: Allocator passed to the vector, takes a dro::details::Node as the template parameter.
The default capacity is (1) and the std::allocator is the default memory allocator.
-
FlatMap<Key, Value, MaxSize> flatMap(size_type capacity = 1, Allocator allocator = Allocator()); -
FlatSet<Key, MaxSize> flatSet(size_type capacity = 1, Allocator allocator = Allocator());The 'MaxSize' parameter is any integral type. In order to optimize for space efficiency, select the size that can store the maximum number of elements required. An extra slot is needed to represent an empty index.
Type Max Capacity uint8_t 255 uint16_t 65,535 uint32_t 4,294,967,295 uint64_t (default) 18,446,744,073,709,551,615
-
mapped_type& at(const key_type& key);Map Only: Throws std::out_of_range if element doesn't exist.
-
mapped_type& operator[](const key_type& key);Map Only: Inserts new element if element doesn't exist.
-
iterator begin();Returns iterator to the first element in sorted order.
-
const_iterator cbegin() const noexcept;Returns constant iterator to the first element in sorted order.
-
iterator end();Returns iterator to one past the last element.
-
const_iterator cend() const noexcept;Returns constant iterator to one past the last element.
-
iterator rbegin();Returns iterator to the last element in sorted order.
-
const_iterator crbegin() const noexcept;Returns constant iterator to the last element in sorted order.
-
iterator rend();Returns iterator to one past the first element.
-
const_iterator crend() const noexcept;Returns constant iterator to one past the first element.
-
[[nodiscard]] bool empty() const noexcept;Checks whether the container is empty.
-
[[nodiscard]] size_type size() const noexcept;Returns the number of elements in the container.
-
[[nodiscard]] size_type max_size() const noexcept;Returns the maximum possible number of elements.
-
[[nodiscard]] size_type capacity() const noexcept;Returns the number of elements that have been allocated.
-
void reserve(size_type new_cap);Reserves additional space for the number of elements specified.
-
void shrink_to_fit();Deallocates all erased elements and shrinks the capacity to equal the size.
-
void clear() noexcept;Sets the size to zero.
-
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& pair);Map Only: Inserts key value pair into map.
-
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const key_type& key);Set Only: Inserts key into set.
-
std::pair<iterator, bool> emplace(Args&&... args);Constructs value in place for map and key in place for set.
-
size_type erase(const key_type& key);Erases element from container, and does NOT deallocate memory.
-
void swap(self_type& other) noexcept;Swaps the contents of two containers.
-
node_type extract(const key_type& key);Extracts the node from the container.
-
void merge(self_type& source);Merges the contents of one container into another.
-
[[nodiscard]] size_type count(const key_type& key) const;Returns the number of elements matching a specific key.
-
[[nodiscard]] iterator find(const key_type& key);Returns an iterator to the element that matches the specific key. Returns end() if doesn't exist.
-
[[nodiscard]] bool contains(const key_type& key) const;Checks if the specific key exists in the container.
-
[[nodiscard]] pair_iterator equal_range(const key_type& key);Returns a range of elements matching a specific key.
-
[[nodiscard]] iterator lower_bound(const key_type& key);Returns an iterator to the first element not less than the given key.
-
[[nodiscard]] iterator upper_bound(const key_type& key);Returns an iterator to the first element greater than the given key.
-
[[nodiscard]] Compare key_comp() const noexcept;Returns the function that compares keys.
-
[[nodiscard]] Compare value_comp() const noexcept;Returns the function that compares keys in object of type value_type.
I made some modifications to the red black tree algorithm to better apply it to a vector container.
- On rotate operations, swapped the node and child location in memory.
- On insert, swapped the uncle and node when the uncle isn't red and is a valid index.
- On erase, swapped the deleted key with minNode, and then swapped to the end of the vector.
- Prefetched the next level node for binary search on inserts and erase.
These benchmarks were taken on a (4) core Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9300H CPU @ 2.40GHz with isolcpus on cores 2 and 3. The linux kernel is v6.10.11-200.fc40.x86_64 and compiled with gcc version 14.2.1.
Most important aspects of benchmarking:
- Have at least one core isolated with isolcpus enabled in Grub.
- Compile with -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
- Use optimal size template parameter for dro::FlatMap. e.g. for a size of 10,000 specify an uint16_t.
Required C++20 or higher.
To build and install the shared library, run the commands below.
$ mkdir build && cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
$ sudo make install
For help with building the red black tree algorithm, I want to cite the following sources:
This software is distributed under the GNU license. Please read LICENSE for information on the software availability and distribution.
Please open an issue of if you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback.
Please submit bug reports, suggestions, and pull requests to the GitHub issue tracker.