Dockerized version of the pgcli tool for postgres.
- Pull the docker image:
docker pull dencold/pgcli - Run the container:
docker run -it --rm dencold/pgcli DB_URL - Or, if you already have a postgres container, you can just do this:
docker run -it --link my-postgres:postgres --rm dencold/pgcli
Note that DB_URL is in the format of:
postgresql://user:password@host:port/dbname
For more information on database connection strings, see the postgres documentation.
For other run options, see the "Running" section, below.
Installing pgcli is a fairly straightforward process, as long as you already have postgres installed, you can generally get away with a straight pip install, however there are some gotchas. For example, on linux there are a host of other dependencies, from the pgcli installation guide:
Pgcli uses psycopg to talk to postgres database. In order to install psycopg, you will need libpq and python-dev installed on your system. Since psycopg is a C extension for Python, a C compiler is needed to install it on your system.
If you are already using docker, life can be a lot easier. You are a simple pull away from getting pgcli on whatever environment you are running:
docker pull dencold/pgcli
There are a number of additional benefits of using a docker container, we'll see these in the next section...
I generally run my development apps with a separate container for the postgres database. Hooking up the database to the application is achieved via docker links. In order to make it easy to use pgcli on any postgres container, I've made a simple docker wrapper for the command. It is smart about pulling in the linked postgres environment variables and makes it easy to use on your own instances.
If you have one of these postgres containers already running, all you need to do is link the postgres container to pgcli. For example, if your postgres container was named my-postgres, you can attach pgcli with this one-liner:
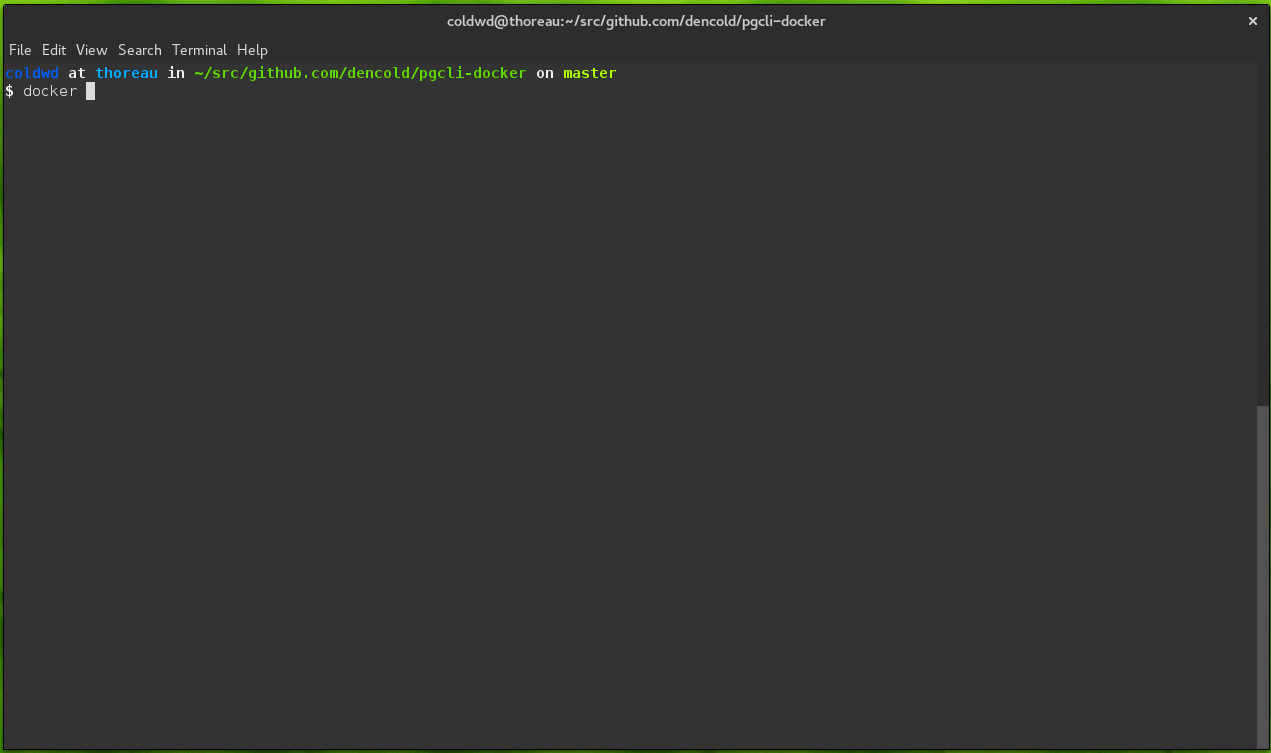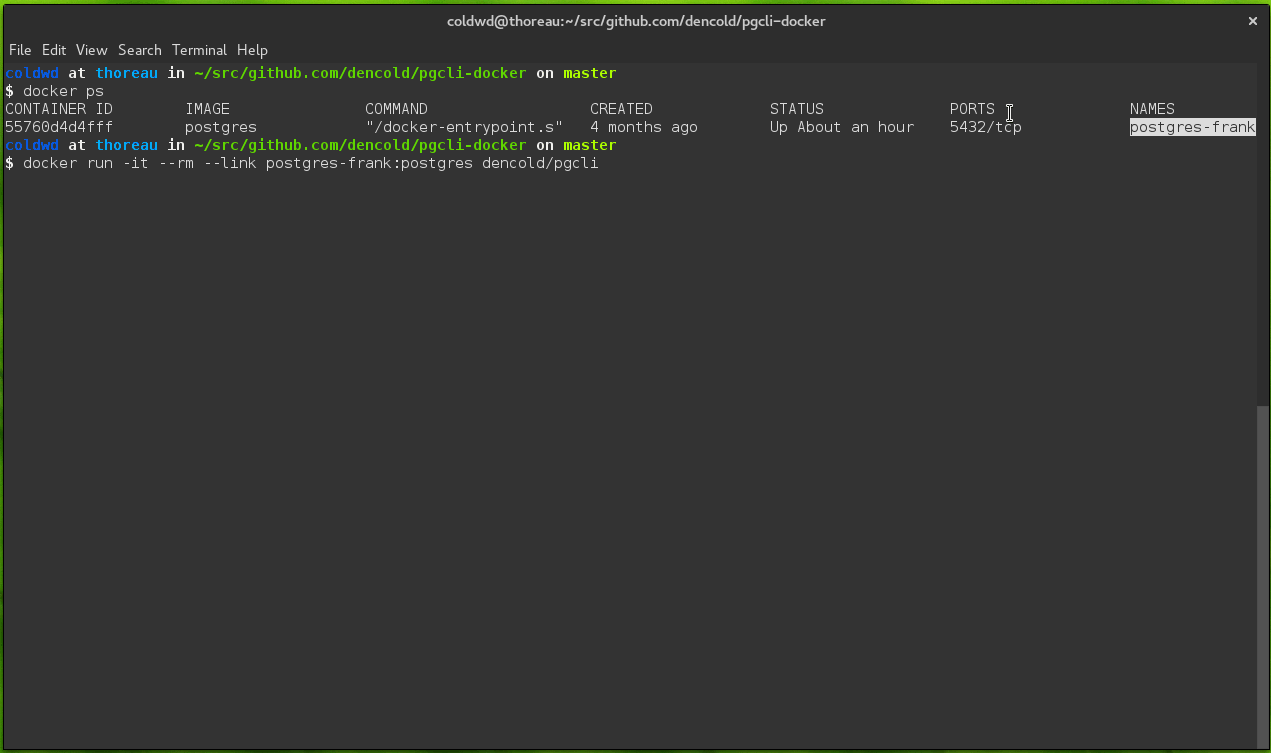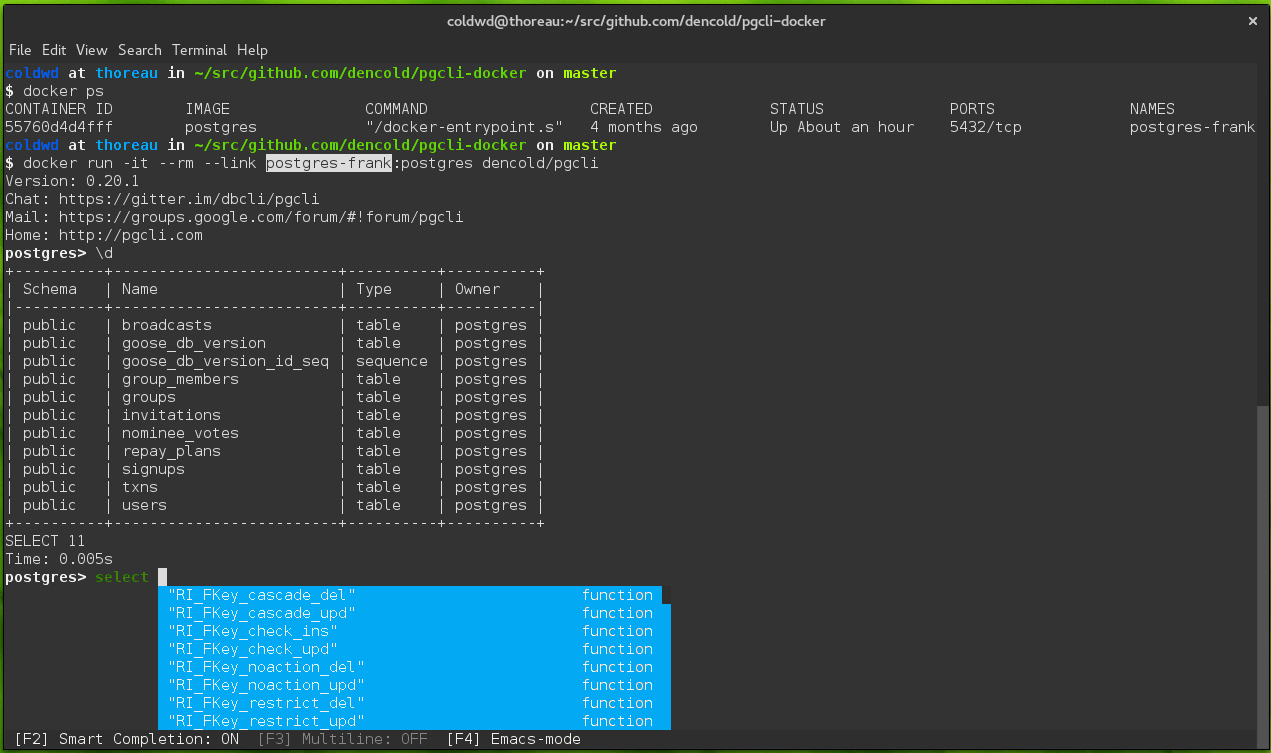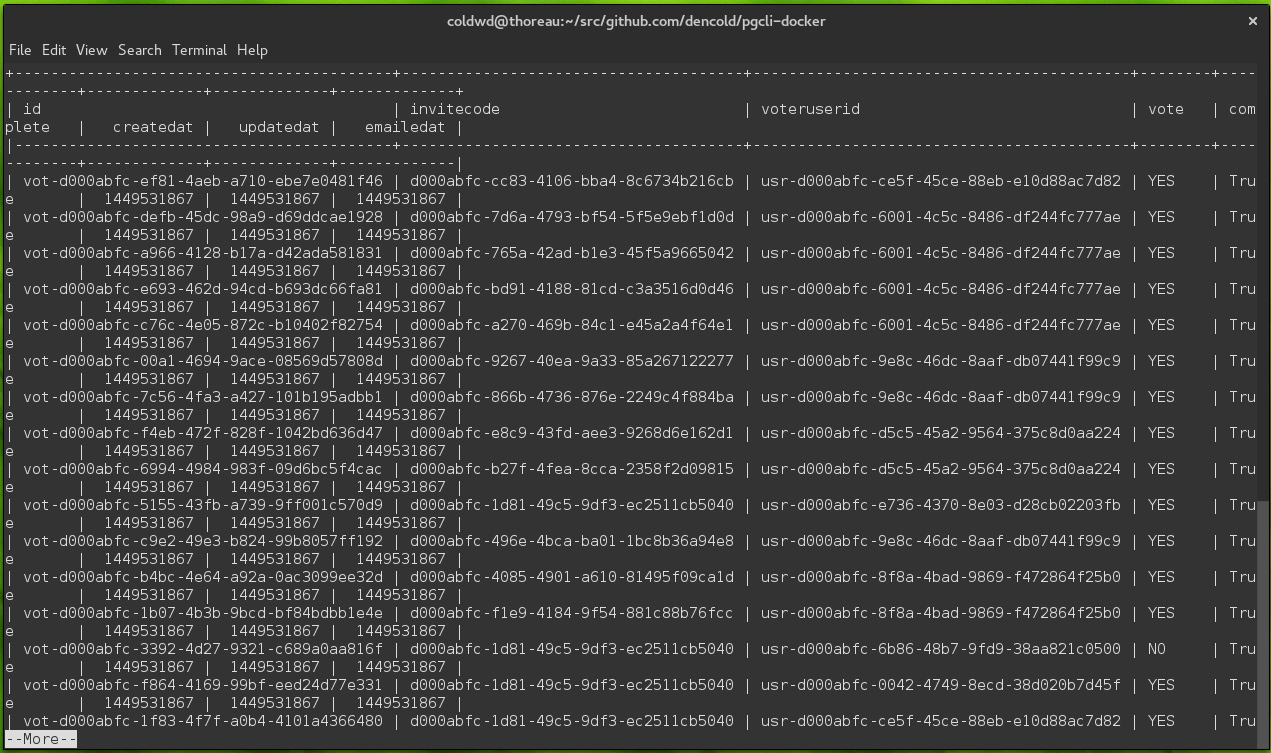
docker run -it --link my-postgres:postgres --rm dencold/pgcli
It will determine host, port, and login details directly from the linked postgres container's environment variables. You should be dropped right into a pgcli session without the need to type in any credentials. Awesomesauce!
This package used to pin pgcli's version to guarantee combatibility, but that's no longer the case. The docker container is created using pip install pgcli so you'll automatically get the latest version of the tool when you run your docker pull.