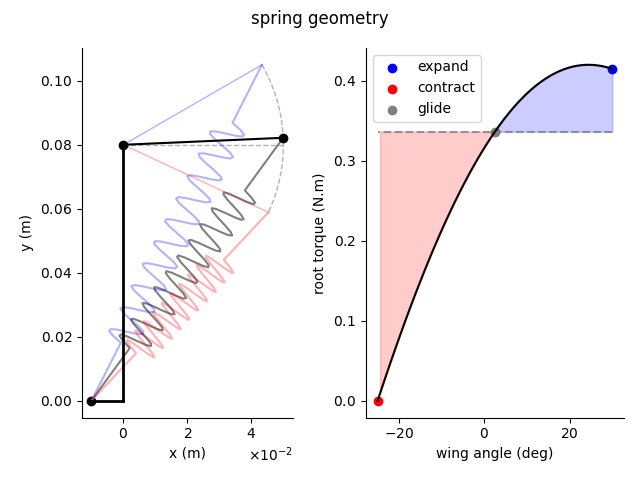
This program calculates various flight parameters for an ornithopter in level flight. The aircraft is modeled as a single set of wings that generate a certain amount of lift and thrust. We estimate the mechanical power required for flight and the electrical power drawn by an electric motor. The lift during gliding flight is also used to estimate the strength of a spring needed to keep the wings from collapsing.
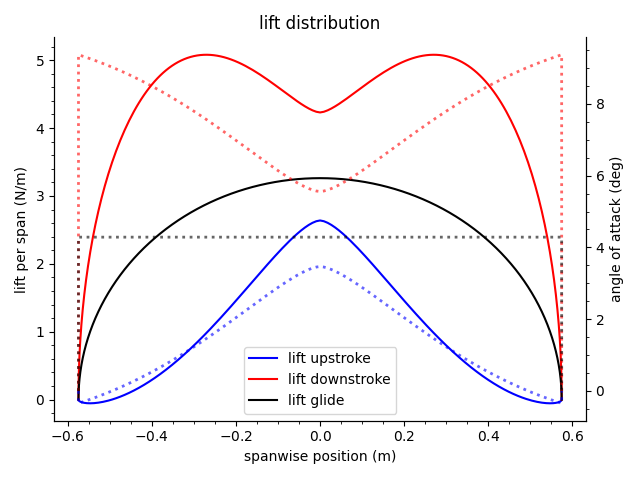
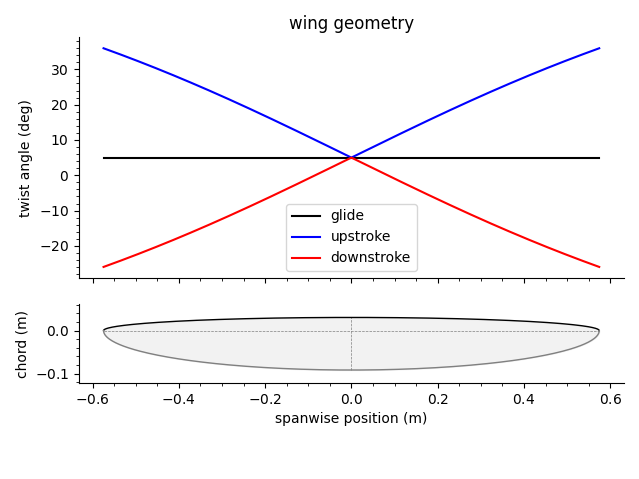
The program outputs a table listing the inputs to the model, along with the values above and other useful parameters. It also generates plots for the lift distribution and twist of the wing during the upstroke, the downstroke, and glide. The wing planform is also shown, in addition to the geometry and torque generated by the spring.
NOTE: This version uses a set of linear equations to solve the lift distributions of the wing. Unfortunately, this form assumes the airspeed is constant across the wingspan (which is not the case for rotating wings). Despite this, the linear form allows the solution to be computed quickly.
The scripts were written in Python 3.9.5 and require the following libraries:
To execute the program, open the terminal/command prompt and browse to the folder containing the interface.py and run the command:
>> python interface.py
If you are using windows, you can simply double click interface.py and to open it with IDLE.
To adjust the calculations, open interface.py with a text editor and change the input variables. These include wing twist as a function of the wingspan, air density, motor voltage, and many other parameters.
-
The aerodynamic forces are calculated according to the paper "Aerodynamic modeling of flapping flight using lifting line theory" by Bhowmik et al.
-
The motor is modeled as an inductor and resistor subject to a constant voltage source and a back emf proportional to the angular velocity. The model is explained in the article "First-Order DC Electric Motor Model" by Mark Drella.
-
The book "How ornithopters fly" by Horst Räbiger was used as a guide to perform the aformentioned calculations.
- Original German text
- French translation (this version was used)
==========================================
INPUTS
==========================================
FLIGHT
------------------------------------------
lift_drag_ratio 4.000 %
amplitude 55.000 deg
dihedral 2.500 deg
gravity 9.810 m/s^2
mass_total 0.300 kg
mass_wing 0.052 kg
air_density 1.204 kg/m^3
area 0.110 m^2
MOTOR
------------------------------------------
voltage 11.100 V
current_stall 6.000 A
current_noload 0.500 A
motor_kv 3100.000 rpm/V
SPRING
------------------------------------------
xoffset -0.010 m
yoffset 0.080 m
radius_spring 0.050 m
==========================================
OUTPUTS
==========================================
FLIGHT
------------------------------------------
power_mechanical 12.361 W
power_aerodynamic 8.151 W
power_inertial 4.210 W
power_minimum 7.155 W
eff_aerodynamic 0.878 %
eff_mechanical 0.579 %
wing_radius 0.574 m
wing_root_chord 0.122 m
frequency 5.998 hz
velocity 9.725 m/s
torque_glide 0.359 N.m
torque_max 0.677 N.m
force_lift 2.943 N
force_thrust 0.736 N
pitch_trim_angle 0.264 deg
MOTOR
------------------------------------------
resistance 1.850 ohm
coeff_power 0.742 %
coeff_angvel 0.754 %
efficiency_motor 0.563 %
power_electric_input 21.948 W
power_max_mechanical 16.650 W
current_motor 1.977 A
gear_ratio 72.071 %
CLIMB
------------------------------------------
climb_rate 0.316 m/s
climb_angle 1.865 deg
SPRING
------------------------------------------
spring_constant 411.314 N/m
spring_force 8.615 N
length_change 0.037 m
spring_angle 56.389 deg