Noise is a decentralized connection (TCP) communication protocol based on a peer-to-peer network. It guarantees anonymity and security of transmitted data, due to several layers of encryption. The name itself to some extent explains how this protocol works, because communication looks in such a way that every peer sends the same package to any peer, which makes it difficult to determine the identity of a particular peer in the network, this huge amount of network traffic can be called a noise.
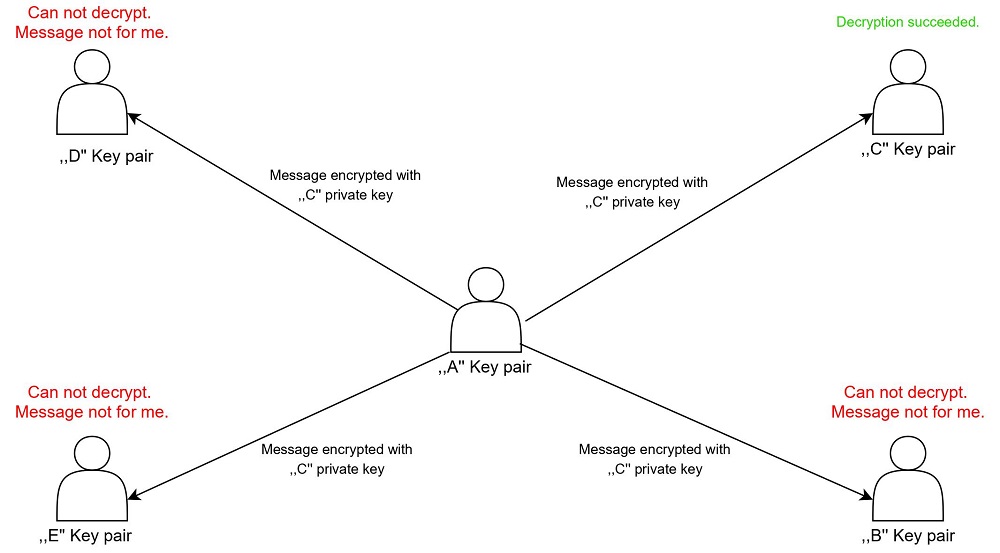
Each peer has a pair of RSA keys. Thanks to this, each message is end-to-end encrypted. The key itself, as in the case of many cryptocurrencies, is treated like a identifier and the problem of "identity proving" in asymmetrical architecture is solved using custom signature systems and private key/RSA signing, but that's not all when it comes to cryptographic functionalities. When sending messages or other packets (MSG/DSC/SGN and KEY packet's), the content of the message is encrypted using AES-GCM. It is worth noting that for each packet the key AES-GCM will be different, in the context of one peer. The key itself is generated using so-called "cryptographically secure random numbers". Later the key to this cipher and the key to the encrypted identity proving signature cipher is encrypted by the public RSA key of the peer, to which we want to send a message. Such a pair of packets is then sent to all known peers. It is worth noting that all local data on the host are also encrypted.
In order to discover new peers, we can add them by hand (public key and IP address) but the protocol itself works so that after connecting to the network, so-called "Discovery" packets are sent. These types of packets work the same way as discussed above message packets, but the content of the payload contains a list of public keys and IP addresses of known hosts. Such packets are then sent to all known peers.
# Installation on Windows
cmd build.cmd
# Update to latest version on Windows
cmd patch.cmd
# Installtion on Linux
chmod +x ./build.sh
sudo sh ./build.sh
# Update to latest version on Linux
chmod +x ./patch.sh
sudo sh ./patch.sh
After running the program, we can use the help command, which will list all available commands. Command list:
- EXIT - Close connections, save local data and exit.
- CLEAR - Clear the screen.
- LIST - List available peer keys, aliases or endpoints.
- SELECT - Select a peer to perform interactions.
- RESET - Reset selected peer.
- SEND(or : symbol for short) - Send message to selected peer.
- SIGN - Send signature to selected peer.
- BLEACH - Reset all signatures related to selected peer.
- REMOVE - Remove a given peer key or a endpoint.
- DISCOVER - Broadcast discovery packets to the network.
- PING - Send a ping packet to a certain endpoint.
- ALIAS - Set alias to certain peer.
- INSERT - Insert new peer key and optional alias or a endpoint.
- HELP - Show available commands.
- INFO - Print information about local peer.
The application was developed using the open-source .NET Core technology. It has no third party dependencies. Only .NET standard libraries are used. Unit testing uses xUnit.
The terminal promot is inspired by the computer found in the game Submchanie 4: The Lab by Mateusz Skutnik. In my opinion, one of the best series of Flash games.