欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/
翻转一棵二叉树。
这道题目背后有一个让程序员心酸的故事,听说 Homebrew的作者Max Howell,就是因为没在白板上写出翻转二叉树,最后被Google拒绝了。(真假不做判断,权当一个乐子哈)
这道题目是非常经典的题目,也是比较简单的题目(至少一看就会)。
但正是因为这道题太简单,一看就会,一些同学都没有抓住起本质,稀里糊涂的就把这道题目过了。
如果做过这道题的同学也建议认真看完,相信一定有所收获!
我们之前介绍的都是各种方式遍历二叉树,这次要翻转了,感觉还是有点懵逼。
这得怎么翻转呢?
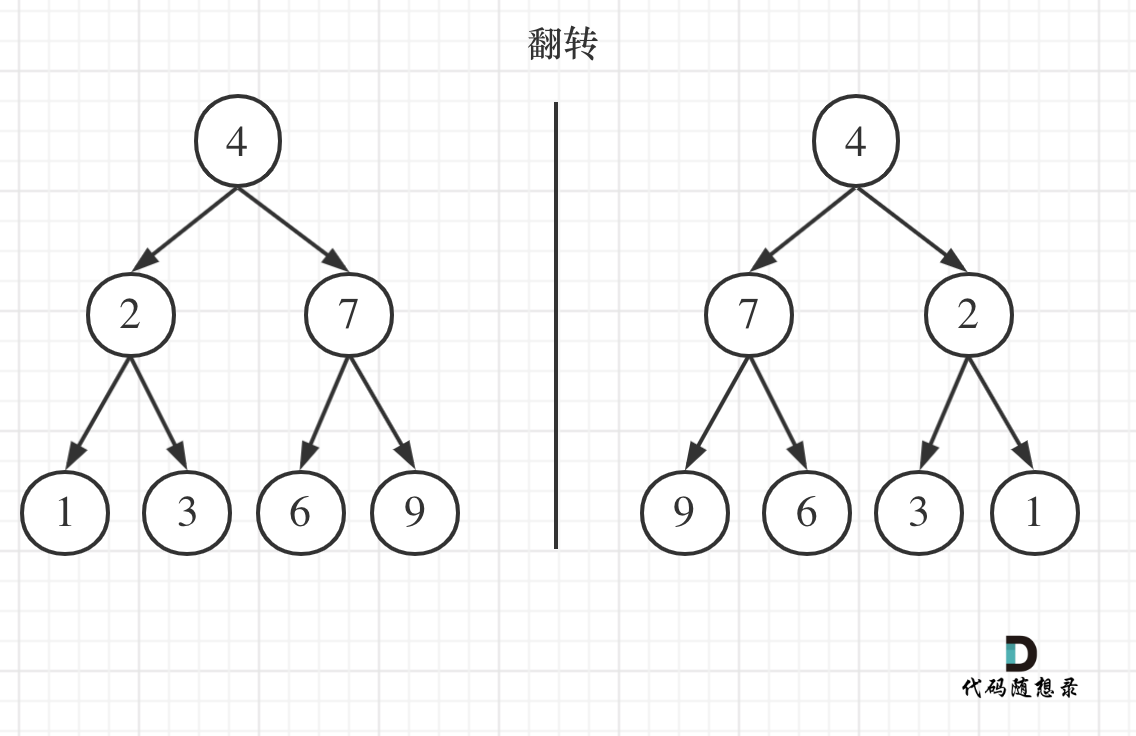
如果要从整个树来看,翻转还真的挺复杂,整个树以中间分割线进行翻转,如图:
可以发现想要翻转它,其实就把每一个节点的左右孩子交换一下就可以了。
关键在于遍历顺序,前中后序应该选哪一种遍历顺序? (一些同学这道题都过了,但是不知道自己用的是什么顺序)
遍历的过程中去翻转每一个节点的左右孩子就可以达到整体翻转的效果。
注意只要把每一个节点的左右孩子翻转一下,就可以达到整体翻转的效果
这道题目使用前序遍历和后序遍历都可以,唯独中序遍历不行,因为中序遍历会把某些节点的左右孩子翻转了两次!建议拿纸画一画,就理解了
那么层序遍历可以不可以呢?依然可以的!只要把每一个节点的左右孩子翻转一下的遍历方式都是可以的!
对于二叉树的递归法的前中后序遍历,已经在二叉树:前中后序递归遍历详细讲解了。
我们下文以前序遍历为例,通过动画来看一下翻转的过程:
我们来看一下递归三部曲:
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数就是要传入节点的指针,不需要其他参数了,通常此时定下来主要参数,如果在写递归的逻辑中发现还需要其他参数的时候,随时补充。
返回值的话其实也不需要,但是题目中给出的要返回root节点的指针,可以直接使用题目定义好的函数,所以就函数的返回类型为TreeNode*。
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root)
- 确定终止条件
当前节点为空的时候,就返回
if (root == NULL) return root;
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
因为是先前序遍历,所以先进行交换左右孩子节点,然后反转左子树,反转右子树。
swap(root->left, root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
基于这递归三步法,代码基本写完,C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中
invertTree(root->left); // 左
invertTree(root->right); // 右
return root;
}
};二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!中给出了前中后序迭代方式的写法,所以本地可以很轻松的切出如下迭代法的代码:
C++代码迭代法(前序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right);
if(node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if(node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
}
return root;
}
};如果这个代码看不懂的话可以在回顾一下二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!。
我们在二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的统一写法中介绍了统一的写法,所以,本题也只需将文中的代码少做修改便可。
C++代码如下迭代法(前序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理逻辑
}
}
return root;
}
};如果上面这个代码看不懂,回顾一下文章二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的统一写法。
也就是层序遍历,层数遍历也是可以翻转这棵树的,因为层序遍历也可以把每个节点的左右孩子都翻转一遍,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};如果对以上代码不理解,或者不清楚二叉树的层序遍历,可以看这篇二叉树:层序遍历登场!
针对二叉树的问题,解题之前一定要想清楚究竟是前中后序遍历,还是层序遍历。
二叉树解题的大忌就是自己稀里糊涂的过了(因为这道题相对简单),但是也不知道自己是怎么遍历的。
这也是造成了二叉树的题目“一看就会,一写就废”的原因。
针对翻转二叉树,我给出了一种递归,三种迭代(两种模拟深度优先遍历,一种层序遍历)的写法,都是之前我们讲过的写法,融汇贯通一下而已。
大家一定也有自己的解法,但一定要成方法论,这样才能通用,才能举一反三!
Java:
class Solution {
/**
* 前后序遍历都可以
* 中序不行,因为先左孩子交换孩子,再根交换孩子(做完后,右孩子已经变成了原来的左孩子),再右孩子交换孩子(此时其实是对原来的左孩子做交换)
*/
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
swapChildren(root);
return root;
}
private void swapChildren(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
}Python:
递归法:前序遍历
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root:
return None
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left #中
self.invertTree(root.left) #左
self.invertTree(root.right) #右
return root迭代法:深度优先遍历(前序遍历)
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root:
return root
st = []
st.append(root)
while st:
node = st.pop()
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left #中
if node.right:
st.append(node.right) #右
if node.left:
st.append(node.left) #左
return root迭代法:广度优先遍历(层序遍历)
import collections
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
queue = collections.deque() #使用deque()
if root:
queue.append(root)
while queue:
size = len(queue)
for i in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left #节点处理
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return rootGo:
func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root ==nil{
return nil
}
temp:=root.Left
root.Left=root.Right
root.Right=temp
invertTree(root.Left)
invertTree(root.Right)
return root
}JavaScript:
使用递归版本的前序遍历
var invertTree = function(root) {
//1. 首先使用递归版本的前序遍历实现二叉树翻转
//交换节点函数
const inverNode=function(left,right){
let temp=left;
left=right;
right=temp;
//需要重新给root赋值一下
root.left=left;
root.right=right;
}
//确定递归函数的参数和返回值inverTree=function(root)
//确定终止条件
if(root===null){
return root;
}
//确定节点处理逻辑 交换
inverNode(root.left,root.right);
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
};使用迭代版本(统一模板))的前序遍历:
var invertTree = function(root) {
//我们先定义节点交换函数
const invertNode=function(root,left,right){
let temp=left;
left=right;
right=temp;
root.left=left;
root.right=right;
}
//使用迭代方法的前序遍历
let stack=[];
if(root===null){
return root;
}
stack.push(root);
while(stack.length){
let node=stack.pop();
if(node!==null){
//前序遍历顺序中左右 入栈顺序是前序遍历的倒序右左中
node.right&&stack.push(node.right);
node.left&&stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(node);
stack.push(null);
}else{
node=stack.pop();
//节点处理逻辑
invertNode(node,node.left,node.right);
}
}
return root;
};使用层序遍历:
var invertTree = function(root) {
//我们先定义节点交换函数
const invertNode=function(root,left,right){
let temp=left;
left=right;
right=temp;
root.left=left;
root.right=right;
}
//使用层序遍历
let queue=[];
if(root===null){
return root;
}
queue.push(root);
while(queue.length){
let length=queue.length;
while(length--){
let node=queue.shift();
//节点处理逻辑
invertNode(node,node.left,node.right);
node.left&&queue.push(node.left);
node.right&&queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return root;
};