Please read the issue guidelines.
Please read the pull request guidelines.
We use the following labels to track issues and PRs:
| Label | Purpose |
|---|---|
type: bug |
bug report confirmed by a plotly team member |
type: regression |
bug that introduced a change in behavior from one version to the next |
type: feature |
planned feature additions |
type: new trace type |
subset of type: feature reserved for planned new trace types |
type: translation |
localization-related tasks |
type: performance |
performance related tasks |
type: maintenance |
source code cleanup resulting in no enhancement for users |
type: documentation |
API doc or attribute description improvements |
type: community |
issue left open for community input and pull requests |
type: duplicate |
self-explanatory |
type: wontfix |
self-explanatory |
status: discussion needed |
Issue or PR that required discussion among maintainers before moving forward |
status: in progress |
PRs that required some initial feedback but not ready to merge |
status: reviewable |
PRs that are completed from the author's perspective |
status: on hold |
PRs that are put on hold |
- git
- node.js. We recommend using node.js v12.x (LTS).
Upgrading and managing node versions can be easily done using
nvmor its Windows alternatives. npmv6.x and up to ensure that thepackage-lock.jsonfile is used and updated correctly.
git clone https://github.com/plotly/plotly.js.git
cd plotly.js
npm installnpm run pretestnpm startThis command bundles up the source files with source maps using browserify, starts a watchify file watcher (making the your dev plotly.js bundle update every time a source file is saved) and opens up a tab in your browser.
A typical workflow is to make some modifications to the source, update the
test dashboard, inspect and debug the changes, then repeat. The test dashboard
comes bundled with some useful tools while developing - all bundled under the
Tabs object:
| Method/Property | Description |
|---|---|
Tabs.fresh([id]) |
Creates a fresh graph div and returns it (default id of graph). |
Tabs.getGraph([id]) |
Returns the default or specified graph div. |
Tabs.plotMock(mock, [id]) |
Plots the specified mock (.json extension is not required). |
Tabs.snapshot([id]) |
Creates a png snapshot of the plot and places it below. |
Tabs.reload() |
Reloads the plotly.js script and will execute Tabs.onReload once completed. |
Tabs.onReload() |
By default, set to noop but you may set Tabs.onReload to any function you wish. This is useful for replotting a mock or test every time you reload the plotly.js script. |
Tabs.purge() |
Destroys all plots. |
View the source for more info.
Three additional helpers exist that are refreshed every second:
gd- this is the default plot divfullData- shortcut togd._fullDatafullLayout- shortcut togd._fullLayout
There is also a search bar in the top right of the dashboard. This fuzzy-searches image mocks based on their file name and trace type.
Use the plotly-mock-viewer
which has live-reloading and a bunch of other cool features.
An online version of plotly-mock-viewer is available at https://rreusser.github.io/plotly-mock-viewer/
which uses https://cdn.plot.ly/plotly-latest.min.js
npm run preprocess: pre-processes the css and svg source file in js. This script must be run manually when updating the css and svg source files.npm run watch: starts a watchify file watcher just like the test dashboard but without booting up a server.
Both jasmine and image tests are run on CircleCI on every push to this repo.
Jasmine tests are run in a browser using karma. To run them locally:
npm run test-jasmine
To run a specific suite, use:
npm run test-jasmine -- <suite>
where the <suite> corresponds to the suite's file name as found in
test/jasmine/tests/.
You can also test multiple suites at a time, for example:
npm run test-jasmine -- bar axes scatter
which will run tests in the bar_test.js, axes_test.js and scatter_test.js
suites.
To turn off the autoWatch / auto-bundle / multiple run mode:
npm run test-jasmine -- <suite> --nowatch
In certain situations, you may find that the default reporting is not verbose enough to pin down the source of the failing test. In this situation, you may wish to use karma-verbose-reporter:
npm run test-jasmine -- <suite> --verbose
For more info on the karma / jasmine CLI:
npm run test-jasmine -- --help
npm run test-jasmine -- --info
Image pixel comparison tests are run in a docker container. For more information on how to run them locally, please refer to image test README.
Running the test locally outputs the generated png images in build/test_images/ and the png diffs in build/test_images_diff/ (two git-ignored directories).
To view the image pixel comparison test results, run
npm run start-image_viewer
which shows the baseline image, the generated image, the diff and the json mocks of test cases that failed.
To view the results of a run on CircleCI, download the build/test_images/ and build/test_images_diff/ artifacts into your local repo and then run npm run start-image_viewer.
- Click on the
DEBUGbutton - In the
DEBUG RUNNERwindow, open the console (e.g. with<ctrl-shift-j>) - Find test file (e.g. with
<ctrl-o>+ typing the name of the file), look out for "bundled" files with the same name. - Set
debuggeron relevant line(s) - Rerun the test suite by refreshing the page (e.g. with
<crtl-r>)
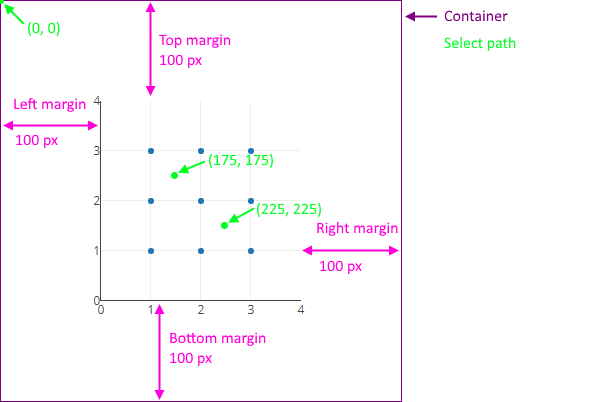
Keep in mind that the interaction coordinates are relative to the top-left corner of the plot, including the margins. To produce a reliable interaction test, it may be necessary to fix the width, height, margins, X axis range and Y axis range of the plot. For example:
Plotly.newPlot(gd, [{
x: [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3],
y: [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],
mode: 'markers'
}], {
width: 400, height: 400,
margin: {l: 100, r: 100, t: 100, b: 100},
xaxis: {range: [0, 4]},
yaxis: {range: [0, 4]}
});This will produce the following plot, and say you want to simulate a selection path of (175, 175) to (225, 225):
- Distributed files are in
dist/ - CommonJS require-able modules are in
lib/ - Sources files are in
src/ - Build and repo management scripts are in
tasks/ - All tasks can be run using
npm run-script - Tests are
test/, they are partitioned intoimageandjasminetests - Test dashboard and image viewer code is in
devtools/ - Built files are in
build/(the files in here are git-ignored, except forplotcss.js)
The trace modules (found in src/traces)
are defined as plain objects with functions and constants attached to them in an index file
(e.g. src/traces/scatter/index.js). The trace modules are "registered" undo the Registry object
(found in src/registry.js) using
Plotly.register (as done in the index files in dist/).
The trace module methods are meant to be called as part of loops during subplot-specific
(e.g. in plots/cartesian/index.js) and figure-wide (e.g. in plots/plots.js) subroutines.
That way, the subroutines work no matter which trace modules got registered.
All traces modules set:
_module.name: name of the trace module as used by the tracetypeattribute._module.basePlotModule: base plot (or subplot) module corresponding to the trace type (e.g.scatterlinks to theCartesianbase plot module,scatter3dlinks togl3d)._module.attributes: JSON-serializable object of attribute declarations. This object is used to generate the plot-schema JSON._module.supplyDefaults: Takes in input trace settings and coerces them into "full" settings undergd._fullData. This one is called during the figure-widePlots.supplyDefaultsroutine. Note that thesupplyDefaultsmethod performance should scale with the number of attributes (not the number of data points - so it should not loop over any data arrays)._module.calc: Converts inputs data into "calculated" (or sanitized) data. This one is called during the figure-widePlots.doCalcdataroutine. Thecalcmethod is allowed to scale with the number of data points and is in general more costly thansupplyDefaults. Please note that some edit pathways skipPlots.doCalcdata(as determined by theeditTypeflags in the attributes files)._module.plot: Draws the trace on screen. This one is called by the definedbasePlotModule.
Other methods used by some trace modules:
_module.categories: list of string identifiers used to group traces by behavior. Traces that have a given category can then be detected usingRegistry.traceIs_module.layoutAttributes: JSON-serializable object of attribute declarations coerced in the layout (e.g.barmodeforbartraces)_module.supplyLayoutDefaults: Defaults logic for layout attributes._module.crossTraceDefaults: Defaults logic that depends on input setting of multiple traces._module.crossTraceCalc: Computations that depend on the data of multiple traces._module.colorbar: Defines the colorbar appearance for traces that support it._module.hoverPoints: Point-picking logic called during hover._module.selectPoints: Polygon-containing logic called during selections._module.style: Sometimes split from_module.plotwhere_module.plotonly draws the elements and_module.stylestyles them._module.styleOnSelect: Optimization of_module.stylecalled during selections._module.convert: Sometimes separated from_module.plotor_module.calcto convert the plotly.js settings to another framework e.g. togl-plot3dforgl3dtraces, tomapbox-glfrommapboxtraces. This split can make the logic easier to test. If you make aconvert, you should call it from eithercalcorplot.
Check if ok, with npm run lint
- See eslintrc and the eslint list of rules for more details.
- Rules listed in the eslintrc file with the ignore flag
0are the recommended rules for new code added.