| layout | background-class | body-class | category | title | summary | image | author | tags | github-link | github-id | featured_image_1 | featured_image_2 | accelerator | demo-model-link | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
hub_detail |
hub-background |
hub |
researchers |
YOLOv5 |
Ultralytics YOLOv5 🚀 for object detection, instance segmentation and image classification. |
ultralytics_yolov5_img0.jpg |
Ultralytics |
|
ultralytics/yolov5 |
ultralytics_yolov5_img1.png |
ultralytics_yolov5_img2.png |
cuda-optional |
Start from a Python>=3.8 environment with PyTorch>=1.7 installed. To install PyTorch see https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/. To install YOLOv5 dependencies:
pip install -U ultralyticsUltralytics YOLOv5 🚀 is a cutting-edge, state-of-the-art (SOTA) model that builds upon the success of previous YOLO versions and introduces new features and improvements to further boost performance and flexibility. YOLOv5 is designed to be fast, accurate, and easy to use, making it an excellent choice for a wide range of object detection, instance segmentation and image classification tasks.
We hope that the resources here will help you get the most out of YOLOv5. Please browse the YOLOv5 Docs for details, raise an issue on GitHub for support, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!
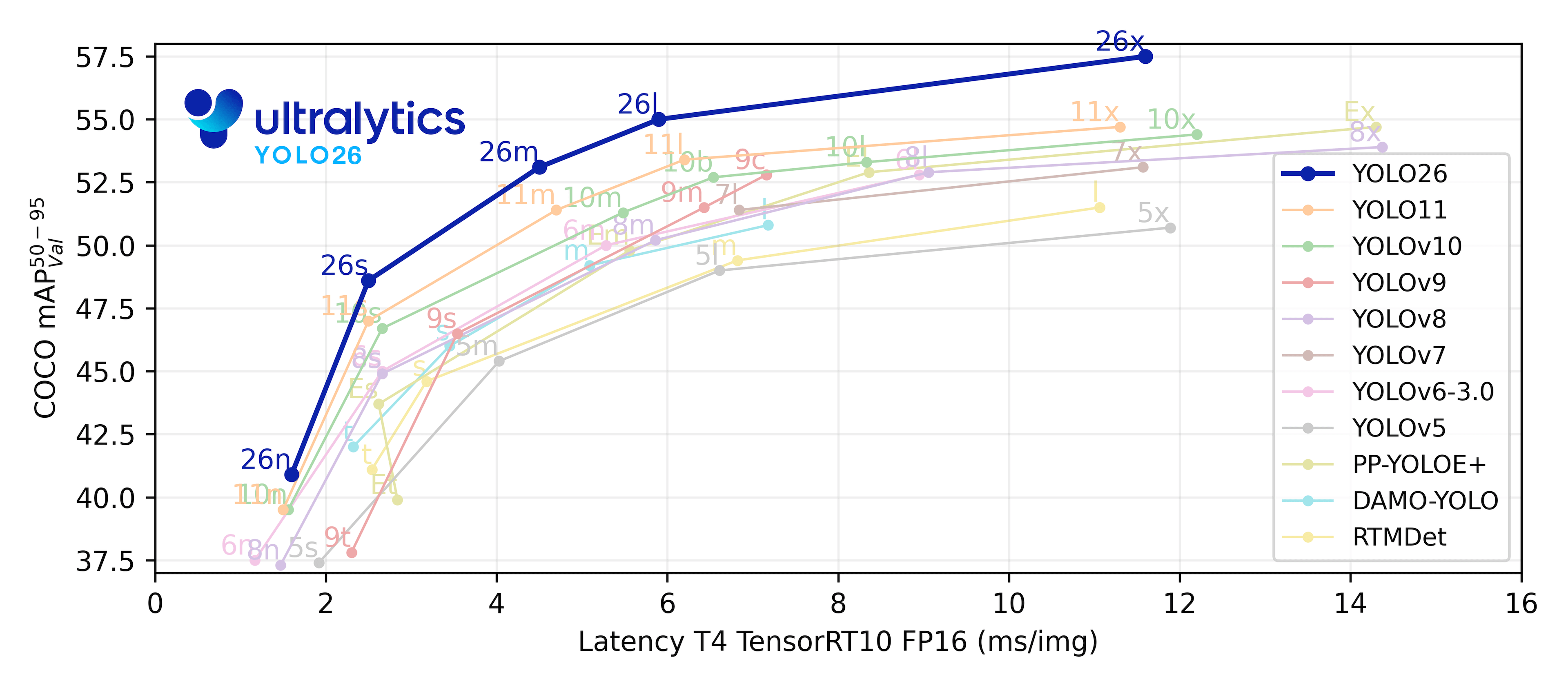
| Model | size (pixels) |
mAPval 50-95 |
mAPval 50 |
Speed CPU b1 (ms) |
Speed V100 b1 (ms) |
Speed V100 b32 (ms) |
params (M) |
FLOPs @640 (B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n | 640 | 28.0 | 45.7 | 45 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 1.9 | 4.5 |
| YOLOv5s | 640 | 37.4 | 56.8 | 98 | 6.4 | 0.9 | 7.2 | 16.5 |
| YOLOv5m | 640 | 45.4 | 64.1 | 224 | 8.2 | 1.7 | 21.2 | 49.0 |
| YOLOv5l | 640 | 49.0 | 67.3 | 430 | 10.1 | 2.7 | 46.5 | 109.1 |
| YOLOv5x | 640 | 50.7 | 68.9 | 766 | 12.1 | 4.8 | 86.7 | 205.7 |
| YOLOv5n6 | 1280 | 36.0 | 54.4 | 153 | 8.1 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 4.6 |
| YOLOv5s6 | 1280 | 44.8 | 63.7 | 385 | 8.2 | 3.6 | 12.6 | 16.8 |
| YOLOv5m6 | 1280 | 51.3 | 69.3 | 887 | 11.1 | 6.8 | 35.7 | 50.0 |
| YOLOv5l6 | 1280 | 53.7 | 71.3 | 1784 | 15.8 | 10.5 | 76.8 | 111.4 |
| YOLOv5x6 + [TTA] |
1280 1536 |
55.0 55.8 |
72.7 72.7 |
3136 - |
26.2 - |
19.4 - |
140.7 - |
209.8 - |
Table Notes
- All checkpoints are trained to 300 epochs with default settings. Nano and Small models use hyp.scratch-low.yaml hyps, all others use hyp.scratch-high.yaml.
- mAPval values are for single-model single-scale on COCO val2017 dataset.
Reproduce bypython val.py --data coco.yaml --img 640 --conf 0.001 --iou 0.65 - Speed averaged over COCO val images using a AWS p3.2xlarge instance. NMS times (~1 ms/img) not included.
Reproduce bypython val.py --data coco.yaml --img 640 --task speed --batch 1 - TTA Test Time Augmentation includes reflection and scale augmentations.
Reproduce bypython val.py --data coco.yaml --img 1536 --iou 0.7 --augment
This example loads a pretrained YOLOv5s model and passes an image for inference. YOLOv5 accepts URL, Filename, PIL, OpenCV, Numpy and PyTorch inputs, and returns detections in torch, pandas, and JSON output formats. See the YOLOv5 PyTorch Hub Tutorial for details.
import torch
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', pretrained=True)
# Images
imgs = ['https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'] # batch of images
# Inference
results = model(imgs)
# Results
results.print()
results.save() # or .show()
results.xyxy[0] # img1 predictions (tensor)
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # img1 predictions (pandas)
# xmin ymin xmax ymax confidence class name
# 0 749.50 43.50 1148.0 704.5 0.874023 0 person
# 1 433.50 433.50 517.5 714.5 0.687988 27 tie
# 2 114.75 195.75 1095.0 708.0 0.624512 0 person
# 3 986.00 304.00 1028.0 420.0 0.286865 27 tieIf you use YOLOv5 or YOLOv5u in your research, please cite the Ultralytics YOLOv5 repository as follows:
@software{yolov5,
title = {YOLOv5 by Ultralytics},
author = {Glenn Jocher},
year = {2020},
version = {7.0},
license = {AGPL-3.0},
url = {https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.3908559},
orcid = {0000-0001-5950-6979}
}For YOLOv5 bug reports and feature requests please visit GitHub Issues, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!