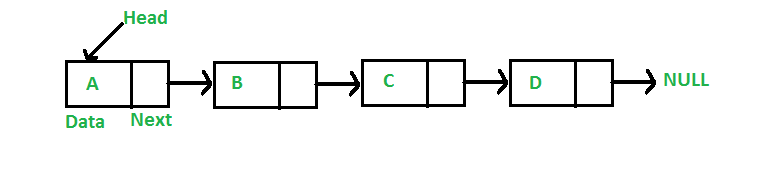
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image:
In simple words, a linked list consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and a reference(link) to the next node in the list.
read more here
Please use this data structure for this project:
/**
* struct list_s - singly linked list
* @str: string - (malloc'ed string)
* @len: length of the string
* @next: points to the next node
*
* Description: singly linked list node structure
*/
typedef struct list_s
{
char *str;
unsigned int len;
struct list_s *next;
} list_t;Write a function that prints all the elements of a list_t list.
- Prototype:
size_t print_list(const list_t *h); - Return: the number of nodes
- Format: see example
- If
strisNULL, print[0] (nil) - You are allowed to use
printf
Write a function that returns the number of elements in a linked list_t list.
- Prototype:
size_t list_len(const list_t *h);
Write a function that adds a new node at the beginning of a list_t list.
- Prototype:
list_t *add_node(list_t **head, const char *str); - Return: the address of the new element, or
NULLif it failed strneeds to be duplicated- You are allowed to use
strdup
Write a function that adds a new node at the end of a list_t list.
- Prototype:
list_t *add_node_end(list_t **head, const char *str); - Return: the address of the new element, or
NULLif it failed strneeds to be duplicated- You are allowed to use
strdup
Write a function that frees a list_t list.
- Prototype:
void free_list(list_t *head);
Write a function that prints You're beat! and yet, you must allow,\nI bore my house upon my back!\n before the main function is executed.
- You are allowed to use the
printffunction
Write a 64-bit program in assembly that prints Hello, Holberton, followed by a new line.
- You are only allowed to use the
printffunction - You are not allowed to use interrupts
- Your program will be compiled using
nasmandgcc: